Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-22 Origin: Site
Molds are a fundamental component in manufacturing and die casting, determining the shape, accuracy, and surface quality of finished parts. Choosing the right mold is critical, as it directly affects production efficiency, overall cost, and the final product’s performance. Among the available options, precision molds stand out for their ability to achieve tight tolerances and high-quality finishes, while standard molds are often sufficient for simpler, non-critical components. This raises an important question for manufacturers and designers alike: when should you use precision molds versus standard molds for your project? Understanding the differences and applications of each type is essential to making the right choice.
Precision molds are specialized molds designed to deliver high accuracy, consistency, and superior surface quality in manufacturing and die casting. They are distinguished by several key characteristics that set them apart from standard molds.
One of the defining features of precision molds is their ability to maintain extremely tight dimensional tolerances, often within ±0.01–0.05mm. This level of precision ensures that parts fit perfectly in assemblies, function reliably, and meet strict industry specifications, especially in automotive and electronics applications.
The cavity surfaces of precision molds are meticulously polished or treated to achieve smooth finishes. This reduces friction during part ejection, minimizes surface defects such as drag marks or scratches, and results in aesthetically superior components. For visible or decorative parts, this smooth finish is critical.
Precision molds incorporate advanced engineering techniques such as mold flow analysis, which optimizes the gating system and material flow to minimize defects like porosity and shrinkage. Additionally, optimized cooling channels ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the mold, reducing internal stress and improving dimensional stability.
Due to their accuracy and quality, precision molds are widely used in industries requiring critical tolerances and excellent surface finish. Common applications include automotive components (engine brackets, key fobs, structural housings), electronics housings, and any visible or high-precision parts where both functionality and appearance are important.
While precision molds are designed for high accuracy and demanding applications, standard molds serve as a more basic and cost-effective solution for simpler manufacturing needs.
Standard molds are conventional molds used in die casting and injection molding processes. They are typically less complex in design and construction, with larger tolerances compared to precision molds. These molds are easier and faster to produce, making them suitable for projects with lower precision requirements or less critical functional demands.
Unlike precision molds, which may achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm, standard molds generally operate within ±0.1–0.3mm. They have simpler cavity designs, fewer advanced features such as optimized cooling channels or detailed gating systems, and require less intricate surface treatments. This simplicity reduces manufacturing time and upfront costs, but may not meet the demands of high-precision or visible components.
Standard molds are ideal for producing basic or non-critical parts where functionality is the primary concern, rather than exact tolerances or aesthetic finish. Typical applications include simple housings, internal brackets, covers, and low-volume production parts. They are also appropriate for components that are not visible to end users and do not require a polished or decorative surface.
Choosing between precision molds and standard molds requires a clear understanding of their key differences in accuracy, surface quality, production efficiency, and cost. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers select the most suitable mold type for their project requirements, ensuring both quality and efficiency.
Precision molds are designed to achieve extremely tight dimensional tolerances, often within ±0.01–0.05mm. This high level of accuracy ensures that parts fit perfectly in assemblies, function reliably, and meet strict industry specifications. In contrast, standard molds typically allow larger tolerances, ranging from ±0.1–0.3mm, which is sufficient for non-critical components but may not satisfy high-precision or visible applications.
The cavity surfaces of precision molds are meticulously polished or treated to deliver mirror-like finishes, reducing friction during part ejection and ensuring superior aesthetics. Standard molds, however, usually have simpler surface finishes that are adequate for internal or non-visible parts but may show minor imperfections on exposed surfaces. This makes precision molds especially important for visible or decorative components.
Precision molds often incorporate advanced features such as multi-cavity designs and optimized cooling channels, enabling high-volume production without compromising quality. Standard molds, with their simpler design, may not support the same level of efficiency in mass production and are typically more suited for small to medium batch runs. Efficient mold design in precision molds also helps reduce cycle times and improve overall manufacturing productivity.
Developing precision molds involves higher initial costs and longer design and manufacturing lead times due to their complexity and tight tolerances. Standard molds are more cost-effective upfront and quicker to produce, making them ideal for projects with budget constraints or less demanding requirements. However, the long-term benefits of precision molds, including reduced rework, lower scrap rates, and consistent part quality, often outweigh the higher initial investment.
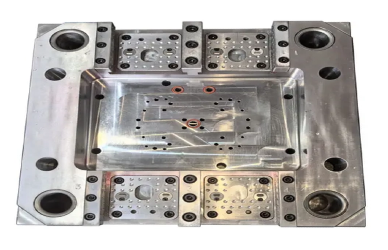
Selecting the right mold for a project requires careful evaluation of multiple factors, especially when considering the advantages of precision molds.
The function of the part is a primary consideration. For load-bearing components, parts with critical tolerances, or visible aesthetic features, precision molds are essential to ensure structural integrity and flawless surface finish. Standard molds may suffice for non-critical or internal parts where appearance and tight tolerances are less important.
High-volume production often benefits from precision molds, as they can maintain consistent quality across thousands of cycles and support multi-cavity designs. Small-batch or low-volume runs may not justify the cost of precision molds, making standard molds a more practical choice.
The type of material used also influences mold choice. Aluminum and zinc alloys, commonly used in automotive and electronics components, often require precision molds to manage shrinkage, porosity, and dimensional accuracy. Magnesium or plastic parts may allow more flexibility, depending on the application.
Precision molds typically involve higher upfront costs and longer lead times due to their complex design and manufacturing requirements. Projects with strict budget or time limitations may need to balance quality and cost, sometimes opting for standard molds for non-critical components.
For industries with rigorous quality standards, such as automotive, adherence to IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 is critical. Precision molds help manufacturers meet these certifications consistently, ensuring reliable performance and regulatory compliance.
In summary, precision molds offer significant advantages over standard molds, including higher accuracy, superior surface finish, and consistent quality, making them ideal for critical, load-bearing, or visible components. Choosing the right mold directly impacts product quality, production efficiency, and overall cost, and can also influence the long-term durability and reliability of the final product. Beyond these benefits, precision molds help manufacturers meet strict industry standards, reduce scrap and rework, and ensure consistent performance across large-scale production runs. To achieve the best results, it is essential to carefully evaluate your project requirements and partner with a qualified mold manufacturer experienced in designing and producing precision molds, ensuring both optimal performance and cost-effectiveness throughout the production process. By investing in the right mold from the start, companies can save time, reduce defects, and deliver high-quality components that meet the most demanding industry expectations.
